Sky's Diamond
Let the stars lead the way.




NASA's Space App Challenge
TWINKLE, TWINKLE, LITTLE STAR
Who we are

Sky's Diamonds is a team created by four undergraduate students under NASA's Space App Challenge.
We are firm believers in data, and its power to guide decisions, spearhead innovation, and create lasting solutions.
We are dedicated to advising forward-thinking people, about stellar variability and helping them them understand how dynamic the night sky really is.
Dimosthenis Minas
Evangelos Kouros
Ioanna Styliani Ellina
Michalis Ioakeimidis
What we offer

Information Tool
Information about stellar variability—how and why the stars in the night sky change.

User- Friendly App
Communication of this knowledge to our audience, with the best possible way.

Addressed to all
Variety of information provided addressed for both students and adults who are interested in this domain.

Quizzes to test your knowledge
Ability to test your knowledge with the aid of quizzes created by people specified in this domain, with different level of difficulty.
Our Users
Schools - Universities
Citizens interested in star variations
Employees in Space Agencys or Space-related companies

Information
Why do stars twinkle?
Brightness of stars






Light curves are graphs that show the brightness of an object over a period of time. In the study of objects which change their brightness over time, such as novae, supernovae, and variable stars, the light curve is a simple but valuable tool to a scientist.



Did you know that stars from space look different than on Earth?
vs

Why do stars twinkle?
As light from a star races through our atmosphere, it bounces and bumps through the different layers, bending the light before you see it. Since the hot and cold layers of air keep moving, the bending of the light changes too, which causes the star’s appearance to wobble or twinkle.
As a result, this gives the illusion that stars twinkle when observed from earth, but the truth is that above earth's atmosphere, stars do not twinkle.
The brightness of stars can vary in terms of increase or decrease over time.
Stars are always changing and their brightness can indicate their change with time
Others are exploding that let us measure the accelerating expansion of the universe: Super Nova
Shine Bright



Unique Stars
Tens of thousands of variable of stars, countless more are yet to be discovered!
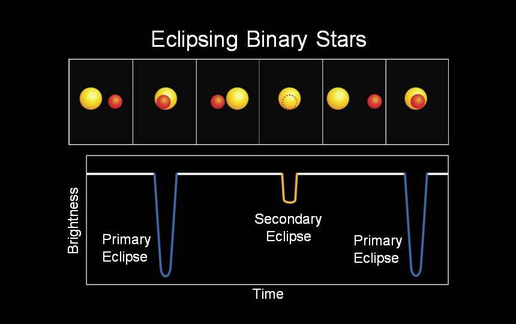
Some stars vary extrinsically: Eclipsing Binary stars
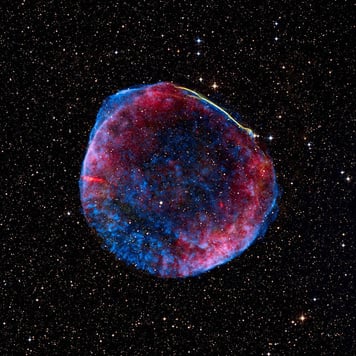
Others are exploding that let us measure the accelerating expansion of the universe: Super Nova
Cepheids, also called Cepheid Variables, are stars which brigthen and dim periodically. This behavior allows them to be used as cosmic yardsticks out to distances of a few tens of millions of light-years.
Cepheids

Cepheids are reasonably abundant and very bright.
Astronomers can identify them not only in our Galaxy, but in other nearby galaxies as well. If one requires the distance to a given galaxy one first locates the Cepheid variables in this galaxy.
From these observations one determines the period of each of these stars.

Cepheids
They can double their brightness over the course of a single week!
1912
Henrietta Swan Leavitt noted that 25 stars, called Cepheid stars, would brighten and dim periodically. She was able to measure the period of each star by measuring the timing of its ups and downs in brightness.
The brighter the Cepheid, the longer its period.
Cepheids : very special variable stars because their period is
- regular (that is, does not change with time), and
- a uniform function of their brightness. That is, there is relation between the period and brightness such that once the period is known, the brightness can be inferred.
Graphs that show the brightness of an object over a period of time. In the study of objects which change their brightness over time, such as novae, supernovae, and variable stars, the light curve is a simple but valuable tool to a scientist.
Images show a scientist where in an object light is emitted. Another piece of information we have about light is when it reaches the detector. The record of changes in brightness that a light curve provides can help astronomers understand processes at work within the object they are studying and identify specific categories (or classes) of stellar events.
The record of changes in brightness that a light curve provides can help astronomers understand processes at work within the object they are studying and identify specific categories (or classes) of stellar events. Light curves can be generated for any measure of brightness which is measured over time.
Cataclysmic variables (CVs) are binary star systems that have a white dwarf and a normal star companion. They are typically small – the entire binary system is usually the size of the Earth-Moon system – with an orbital period of 1 to 10 hours.
The white dwarf is often referred to as the "primary" star, and the normal star as the "companion" or the "secondary" star. The companion star, a star that is "normal," like our Sun, loses material onto the white dwarf via accretion.
More than a MILLION of these cataclysmic variables in the galaxy, but only those near our Sun (several hundreds) have been studied in X-rays so far.
Classical novae are seen to erupt once, and the amplitude of the outburst is the largest among CVs. They are caused by a sudden nuclear fusion of hydrogen-rich material on the surface of the white dwarf.
Dwarf novae outbursts are smaller in amplitude and higher in frequency than classical novae.